 |
| Click to enlarge |
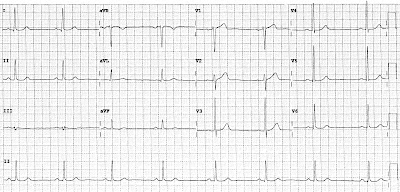
- 48 bpm
- Sinus arrhythmia
- Sinus rhythm
- Normal
- PR - Normal (~200ms)
- QRS - Normal (80ms)
- QT - 410ms (QTc Bazette 370ms)
- Early R wave transisition
- Borderline voltage criteria LVH
- V1 S + V5 R ~35mm
- No non-voltage criteria present
- Sinus bradycardia with sinus arrhythmia
I get asked to review many ECG's that show sinus bradycardia and there are a few considerations in these cases including:
- Is the patient symptomatic ?
- Is this 'normal' for the patient ?
- What is / could be the cause ?
Regarding symptoms these may be the reason for an Emergency Department attendance or more insidious and can include:
- Syncope
- Dizziness
- Light headedness
- Dysponea
- Decreased exercise tolerant
- Lethargy
- Palpitations
- Chest pain
There are multiple potential causes of bradycardia including:
- Physiological - athletes or during sleep
- Increased vagal tone - nausea, vomiting, pain
- Ischaemia
- Drug effect / toxicity - inc, digoxin, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers
- Environmental - hypothermia
- Endocrine - hypothyroid
- Myocarditis
- Sinus node dysfunction
- Sleep apnoea
References / Further Reading
Life in the Fast Lane
Textbook
- Chan TC, Brady WJ, Harrigan RA, Ornato JP, Rosen P. ECG in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care. Elsevier Mosby 2005.
No comments:
Post a Comment